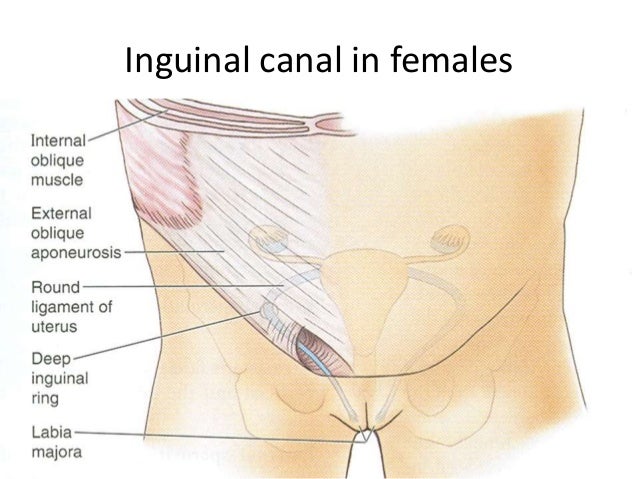
Recently, a study hit my inbox about Endometriosis mimicking an inguinal hernia. So, of course, my interest was piqued and research had to take place! Be warned, though, it’s considered VERY rare. In all the literature I’ve read, only 42 cases have been referenced as being documented inguinal Endo. But when has rarity stopped me from sharing something about Endometriosis? Yeah. Never. Here we go!
What is AN inguinal hernia?
An inguinal hernia is the most common type of hernia (about 70% of hernias are inguinal) and usually manifests as a small lump in the groin area. Both men and women can get inguinal hernias, but it’s apparently more common in men. It occurs if there’s a small hole in your abdominal cavity which allows fat or intestines to seep through, which can a lump or swelling to occur.
Continue reading

